Example Gallery¶
This gallery contains a number of usage examples and case studies to highlight the ease-of-use and flexibility of pulse2percept.
Implants¶
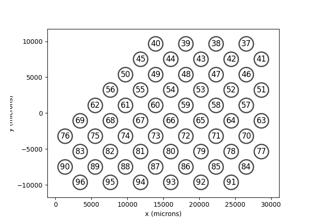
The implants module provides access to various
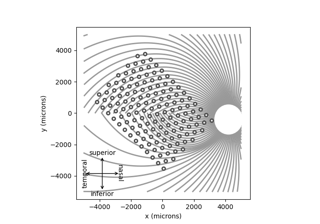
state-of-the-art retinal prostheses, such as
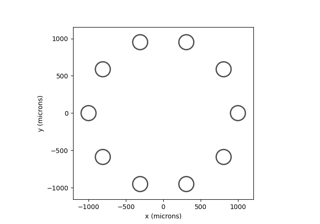
ArgusI and
ArgusII (epiretinal),
Alpha-IMS and
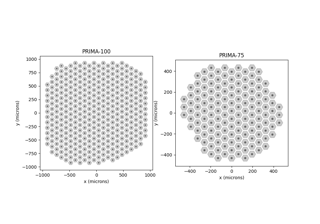
PRIMA (subretinal),
as well as BVT24 (suprachoroidal).
Other implants can be added by creating a new
ProsthesisSystem object.
Stimuli¶
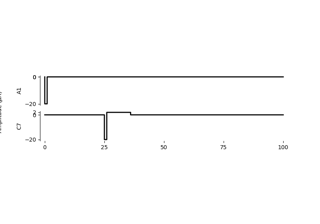
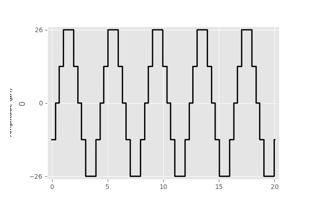
The stimuli module provides a number of common
electrical stimulus types, such as
BiphasicPulseTrain,
which can be assigned to electrodes of a
ProsthesisSystem object.
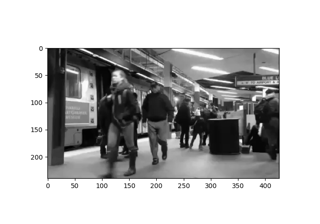
Stimuli can also be created from images
(ImageStimulus) and videos
(VideoStimulus).
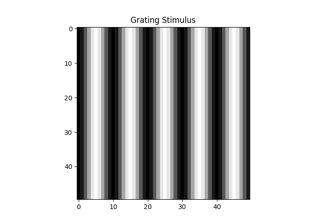
Generating a drifting sinusoidal grating or drifting bar stimulus
Models¶
The pulse2percept.models module provides a number of published and
verified computational models that can be used to predict neural responses or
visual percepts resulting from electrical stimulation, such as
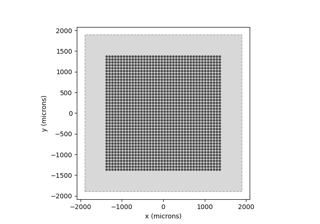
Nanduri2012Model and
AxonMapModel.
New models can be created by mixing-and-matching spatial and temporal models, or by creating a new one from scratch.
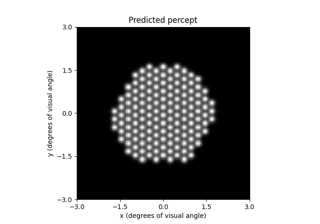
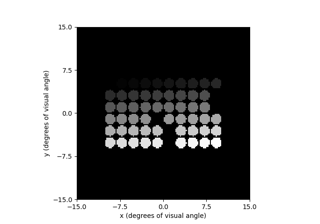
Beyeler et al. (2019): Focal percepts with the scoreboard model
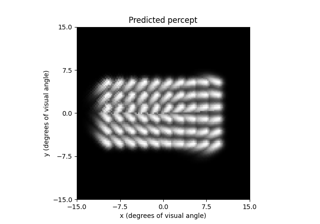
Beyeler et al. (2019): Axonal streaks with the axon map model
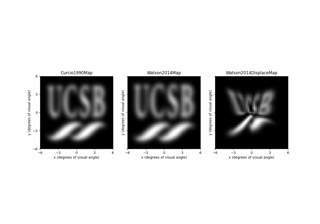
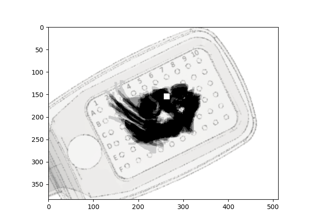
Predicting the perceptual effects of different visual field maps
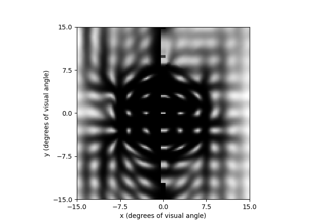
Neuropythy and Neuralink: Patient specific visual field maps based on MRI
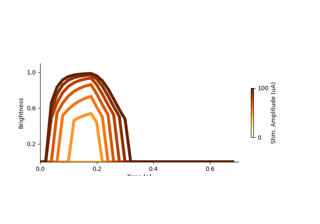
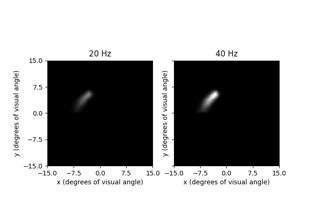
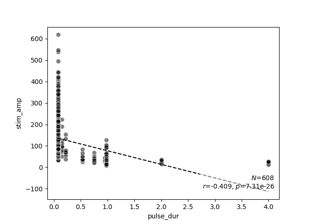
Granley et al. (2021): Effects of Biphasic Pulse Parameters with the BiphasicAxonMapModel
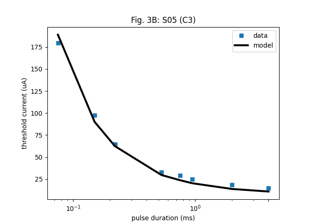
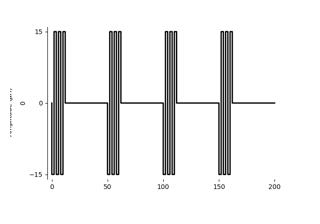
Horsager et al. (2009): Predicting temporal sensitivity

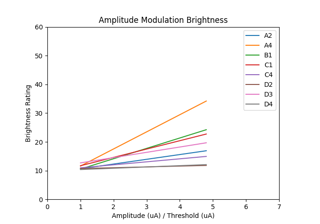
Nanduri et al. (2012): Frequency vs. amplitude modulation
Datasets¶
The pulse2percept.datasets module provides helper functions
that can be used to load datasets from the bionic vision community,
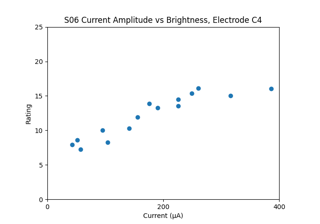
such as load_horsager2009,
fetch_beyeler2019,
load_nanduri2012 and
load_fornos2012.
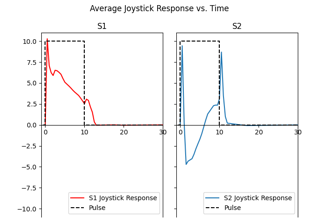
Phosphene fading data from Perez Fornos et al. (2012)